What is a sensor?
Sensor is a device that measure or detects a physical property and record, indicates or otherwise respond to it.
Industrial sensors
sensors are also examples of transducers.(transducer is a device that converts one physicalquantity into another quantity like voltage ..etc. ) . This sensor technology is highly using in local Industry and in world industry .Here are some types of sensors which are highly using in industry.
Proximity Sensors
- mechanical
- Optical
- Inductive/ Capacitive
- Ultra Sonic
Position/Velocity
- Potentiometer
- LVDT
- Encoders
- Resolvers
- Tacho generator
Force/Pressure sensors
Vibration/acceleration
Sound sensors
pyrometers
Vibration/acceleration
Sound sensors
pyrometers
Proximity Sensors
Widely use in general industrial automation.
Proximity is maiainly consist of four parts- Sensor head
- Ditector circuit
- Amplifier
- Output
Catagarization of proximity sensors
Mechanical proximity switches
Capable for ON/OFF operation only. Have two general modes. Very simple operation.
- NC- normal close
- NO-normal open
usually used as:
- Limit switches
- Presence /absence indicator
- Door closed / open
 |
| proximity sensors |
 |
| usage of proximity sensors |
Optical Proximity Sensors
Optical proximity sensor is consists of mainly 3 parts
- Transmitter
- Receiver
- Amplifier relay
A infra-red light beam is produced by emitter. This beam is sensed by receiver at another end. The emitter and the detector can be a single unit or not according to the type of the optical proximity. When this beam is interrupted by object, the receiver signal gets changed and another signal is produced.
There are three basic type of photoelectric / Optical sensors.
1- Through beam type
Detection occurs when the target crosses the beam between transmitter and receiver. The transmitter and the receiver are kept in different places.
Features:
- Long-detecting distance (up to 20m)
- Stable detection
- Opaque objects are detectable regardless of shape, colour or material
- Powerful beam
Usage of this type :
- Conveyer /material handling
- Truck height control
2- Retro- reflective photoelectric sensors
In this case both transmitter and the devise is in same component. Detection occurs when the target crosses the beam between sensor head and reflector. Receiver get the reflected beam since the system is available with a retro mirror to do the reflection.
Features:
- Reflector allows for installation in a limited space
- Simple wiring
- Easily-adjustable optical axis
- Opaque objects are detectable regardless of shape, colour, or material

Usage of this type :
- Bottle counters
3- Diffuse reflective
Diffuse sensors sense light returning from the object to be detected and switch the output when it senses.
Features:
- Space-saving
- Adjustment of optical axis not required
- Reflective transparent objects are detectable
- Colour differentiation possible
Ultrasonic Proximity Sensors
Ultrasonic sensors operate by emitting and receiving high-frequency sound waves. The frequency is usually in the order of 200 kHz, which is too high for the human ear to hear.
Modes of Operation
There are two basic modes of operation,
- Opposed mode
- Diffuse mode (echo) mode.
Opposed mode :
In opposed mode, one sensor emits the sound wave and another, mounted opposite the emitter to receive the reflected sound wave.
In diffuse mode, the same sensor emits the sound wave and then listen for the echo that bounces off an object.
Sensing range:
The sensing range is the distance within which the ultrasonic sensor will detect a target under fluctuations of temperature and also the measurements depend on the state of the medium transmitting the sound.
Blind Zone
In the blind spot, objects cannot be detected, or they even may cause error signals. The size of the blind zone depends on the frequency of the transducer. Object located within the blind spot cannot be reliably detected.
Inductive Proximity sensors

Inductive proximity sensors are used for non-contact detection of metallic objects and they are operate under the electrical principle of inductance.
Their operating principle is based on a coil and oscillator that creates an electromagnetic field in the close surroundings of the sensing surface.
An inductive proximity sensor has four components;
The coil, oscillator, detection circuit and output circuit.
The oscillator generates a fluctuating magnetic field in the coil which is located in the device sensing face. When a metal object moves into the inductive proximity sensor’s field of detection, Eddy circuits build up in the metallic object and generate their own magnetic field. These fields have interaction with the coil through mutual inductance. This cause reduce the self-field of the inductive sensor and then the detection circuit of the sensor monitors the oscillator’s strength and triggers an output from output circuitry when the oscillator becomes reduced to a sufficient level.
The coil, oscillator, detection circuit and output circuit.
The oscillator generates a fluctuating magnetic field in the coil which is located in the device sensing face. When a metal object moves into the inductive proximity sensor’s field of detection, Eddy circuits build up in the metallic object and generate their own magnetic field. These fields have interaction with the coil through mutual inductance. This cause reduce the self-field of the inductive sensor and then the detection circuit of the sensor monitors the oscillator’s strength and triggers an output from output circuitry when the oscillator becomes reduced to a sufficient level.
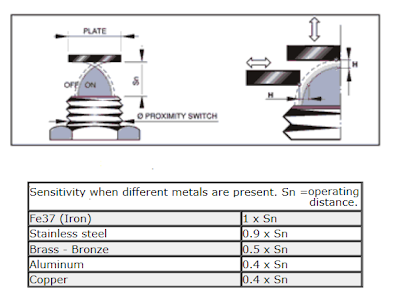
Operating Distance
Its clear that , according to the type of the metallic object change of oscillator’s strength may differ. But we can maintain this clearance according to the table below.
Capacitive Proximity sensors
Capacitive sensors are primarily used when the object to be detected is non-metallic. (both metallic and non-metallic )
The main difference between the capacitive proximity and the inductive proximity is that capacitive proximity sensors produce an electrostatic field Instead of an electromagnetic field. The most common materials sensed are: plastic, glass, wood and paper. Another common application is as a liquid level controller.
Capacitive proximity switches contain 4 main components:
1- Plate
2- Oscillator
3- detection circuit
4- solid state switch
 |
| Construction of sensing face of the Inductive proximity |
When a metallic object is placed near the capacitive sensor's face, the object become an another plate and forms two capacitors. This condition increases the capacitance value so that the value is high enough to cause the sensors internal circuit to oscillate. When a Non-metallic material such as a solid or liquid is located near the sensor head , the capacitance value increases because the object dielectric constant is greater than the air.
In above both cases ,the trigger circuit reads the oscillator’s amplitude and when it reaches a pre-set level the output state of the sensor changes. As the target moves away from the sensor the oscillator’s amplitude decreases, switching the sensor output back to its original state.